Abstract
Introduction: Previously, we assessed the economic burden of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) among Medicare patients and found that the economic burden of relapse is high, at approximately 1.2 and 1.6 times the monthly per-patient costs associated with early and late post-remission therapy, respectively (Tabah A, et al. Blood 2020:136(suppl 1):45). A notably high proportion of patients (55%) received ≥ 1 cycle of a hypomethylating agent (HMA). Therefore, the objective of this study was to assess the economic burden of AML among a subgroup of elderly patients who received only HMA monotherapy during induction and then achieved disease remission. Healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and costs associated with various phases (ie, induction, post-remission therapy, and post-relapse) were assessed.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, which comprised Medicare claims (parts A, B, and D from 2007 through 2016) and the US National Cancer Institute's SEER database (cancer diagnoses from 2007 to 2015). Included patients had an AML diagnosis in the SEER registry, were ≥ 65 years of age at the AML diagnosis date, had initiated HMA (and no other active treatment) in the outpatient (OP) setting during the first induction cycle post-AML diagnosis, and had an International Classification of Diseases, Ninth/Tenth Revision (ICD-9/10) diagnosis code for AML remission following the initiation of induction therapy. Patients were excluded if they had another blood malignancy (including a history of myelodysplastic syndromes), had received hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, or were enrolled in a clinical trial.
The induction therapy period was defined as the first initiation of HMA post diagnosis (index date) to the end of the cycle during which a patient had a code for AML remission. The 6-month period prior to the index date was defined as the baseline period. The post-remission phase ended at the earliest of relapse or end of follow-up (ie, death, end of eligibility, or end of available data [December 31, 2016]). The post-relapse phase was from the date of first AML relapse ICD-9/10 code after remission to the end of follow-up.
Patient characteristics during the baseline period were summarized descriptively. HCRU and costs (adjusted to 2019 US dollars) associated with induction and post-remission therapy were assessed during days that were part of a treatment cycle. The average per-patient monthly HCRU and costs were reported for the induction, post-remission, and post-relapse phases.
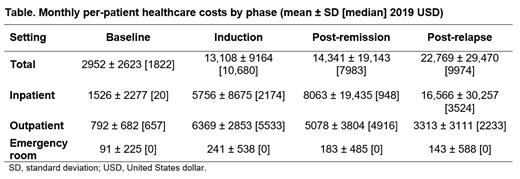
Results: A total of 71 patients with newly diagnosed AML (azacitidine: n = 31; decitabine: n = 40) received HMA induction therapy and achieved remission. The median age at AML diagnosis was 78.8 years, 50.7% of patients were male, and 85.9% were White. The mean ± standard deviation (median) time from index date to the end of follow-up was 16.0 ± 12.3 (14.0) months. A total of 63.4% of patients (n = 45) received post-remission therapy. Among all patients, 43.7% relapsed and 85.9% died by the end of follow-up. OP visits were the most common type of visit across all phases with 95.6% of patients having ≥ 1 OP visit during post-remission therapy and 83.9% during the post-relapse phase. Inpatient (IP) visits were highest in the post-relapse phase with 77.4% of patients having ≥ 1 IP visit. The monthly mean per-patient healthcare costs were highest for the post-relapse phase, followed by post-remission therapy, and induction (Table). Costs associated with the OP setting were the greatest contributor to the induction costs (48.9%) while costs associated with the IP setting were the drivers of the costs in the post-remission therapy (56.2%) and post-relapse (72.8%) phases.
Conclusions: The economic burden of AML treated with HMA induction therapy was highest in the post-relapse phase, at approximately 1.7 and 1.6 times the monthly per-patient costs during the induction and post-remission therapy phases, respectively. In addition, IP costs made up nearly two-thirds of total monthly per-patient costs in the post-relapse phase, up from approximately 44% and 56% of the induction and post-remission therapy phases, respectively. Treatment options that extend the post-remission phase would reduce the high economic burden associated with AML relapse.
Brunner: Celgene, Forty Seven Inc, Jazz: Other: Advisory Board; Novartis, Celgene, Takeda, AstraZeneca: Research Funding. Huggar: Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Copher: Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Zhou: Sanofi: Research Funding; Analysis Group: Current Employment, Other: Employee of Analysis Group which received consulting fees for this project . Zichlin: Analysis Group, Inc.: Consultancy, Current Employment; GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding. Anderson: Analysis Group, which received consultancy fees from GSK: Consultancy, Current Employment. Downes: nalysis Group (employment), Bristol Myers Squibb (consultancy): Consultancy, Current Employment. McBride: BMS: Current Employment.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal